In recent times, the world has been crippled with one of the most fatal pandemics, the SARS-nCoV-2 or the COVID-19. In such a scenario, leading pharma companies and scientists are in a race to develop a cure for the disease. Mesenchymal stem cells or the use of MSCs form one such treatment strategies against COVID-19. In this regard, the present article provides an exhaustive overview on the use of MSCs for the treatment of COVID-19.
Pathogenesis Of COVID-19
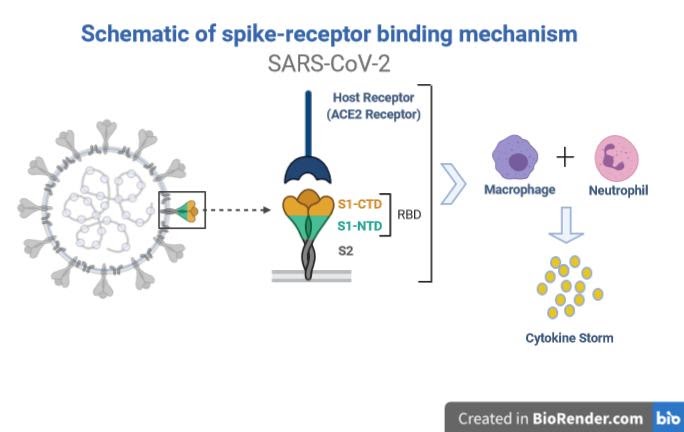
Figure 1: Receptor-spike protein interaction. (Adapted from Golchin A et al.)
Note: CTD: C-Terminal Domain; NTD: N-Terminal Domain; RBD: Receptor-Binding Domain
The pathogenesis (Fig. 1) of SARS-CoV-2 is mainly deployed through its Spike (S) protein. The S protein of the virus identifies angiotensin-I converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and enters the cell of its host. Once into the cell, the immune system of the body produces a large number of cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, GSCF, IP10, MCP1, MIP1A, and TNFα) in an attempt to kill the virus. The release of these inflammatory factors results in a severe cytokine storm, a phenomenon that leads to edema, multiple organ dysfunction syndromes (MODS), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), immune cell depletion and death. (1-3)
Until now, there is no consensus among healthcare authorities on the clinical classification of COVID-19, however, most agree that the disease range between its mild to severe or critically severe forms. (4,5)
Note: ACE-2 receptors are present in the heart, liver, AT2 of lungs, digestive organ, kidney, and in almost all endothelial and smooth muscle cells.
IL: Interleukin; GSCF: Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor; IP: Induced Protein; MCP: Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein; MIP: Macrophage Inflammatory Proteins; TNF: Tumor Necrosis Factor
Role Of Stem Cells In Fight Against COVID-19
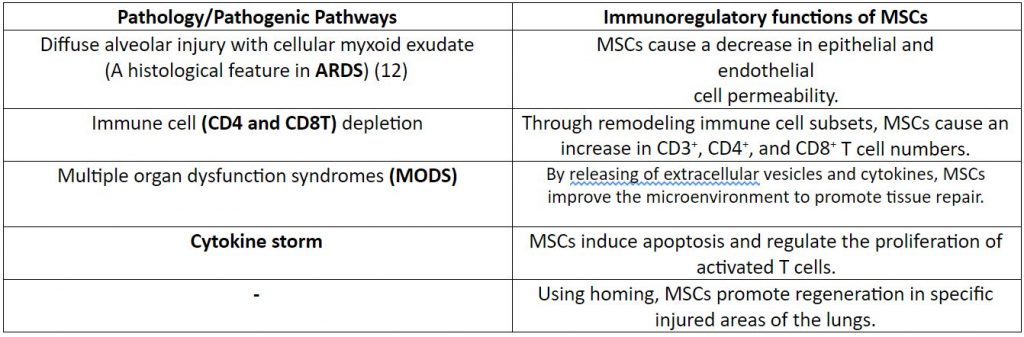
At present, Remdesivir is the only drug to obtain an ‘emergency use authorization’ from the USFDA. However, there is limited information about its safety and efficacy. (6) Therefore, one needs to consider alternatives to the use of Remdesivir. The use of MSCs via intravenous infusion (most preferred route) has shown to be safe and effective in the treatment of COVID-19 via immunoregulatory functions (1, 7-10) as described in Table 1.
Table 1: Response of MSCs to the pathogenic pathways responsible for COVID-19
Clinical Evidence Supporting The Use Of MSCs In COVID-19
Currently, only a handful number of pre-clinical trials have investigated the effects of MSC on animal models of respiratory virus infections. Furthermore, these studies are limited to influenza viruses and have produced conflicting results. Thus such a situation demanded the use of MSCs in human subjects (Table 2) affected with coronavirus respiratory infections.
Table 2: Evidence on the use of MSCs for the treatment of COVID-19. (8,12)
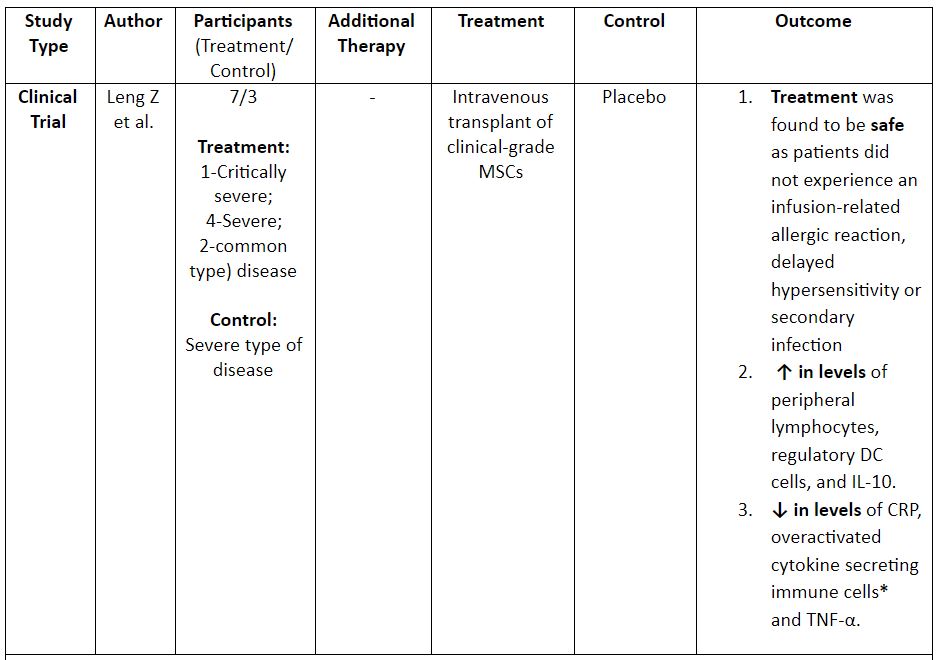
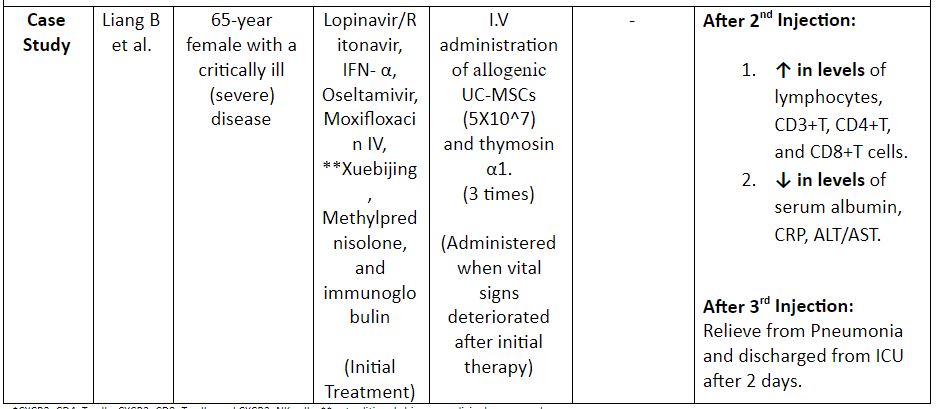
*CXCR3+CD4+T cells, CXCR3+CD8+T cells, and CXCR3+NK cells; ** a traditional chinese medicinal compound
Note: DC: Dendritic Cells; UC-MSCS: Umbilical Cord MSCs; IFN: Interferon; CRP: C – Reactive Protein; ALT: Alanine Aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate Aminotransferase; I.V: Intravenous
A comprehensive analysis of the trials showed that intravenous MSCs were safe and effective for the treatment of patients with severe or critically severe forms of the disease. However, one needs to consider the results of the current on-going trials to fully ascertain the above fact.
Presently there are around 20 clinical trials (n) that are in the research pipeline for furthering our knowledge on the role of MSC in COVID-19. (7) These trials can be categorized as those using:
- MSCs (n=8, involving around 396 participants)
- MSC-derivatives (n=12; involving around 561 participants)
Furthermore, some of the potential sources of MSCs used in these trials include, UC-MSCs, UCB-MSCs, UC-Wharton’s Jelly MSCs, UC-MSCs-CM, AT-MSCs Exo. Further information about the ongoing clinical trials can be obtained from the World Health Organization-International Clinical Trial Registry Platform (WHO-ICTRP).
Note: UCB-MSCs: Umbilical Cord Blood MSCs, CM: Conditioned Medium, AT-MSCs Exo: Adipose tissue-MSCs Exosomes.
Conclusion
The global pandemic has resulted in a pressing need for novel therapies. In this context, it becomes essential to cautiously and carefully utilize the limited available data available along with, upholding high standards of the rationale and appropriately designed investigations to avoid any potential abuse of stem cells in these desperate times.
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to honor the efforts of healthcare workers, the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT), the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR), and other scientific organizations that have taken leadership positions in this arena. He would also like to thank Sara Ahmed Zaki, (Freelance Medical Writer; Egypt) for helping out with the peer-review of the article.
References
- Atluri S, Manchikanti L, Hirsch JA. Expanded Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells (UC-MSCs) as a Therapeutic Strategy in Managing Critically III COVID-19 Patients: The Case for Compassionate Use. Pain Physician. 2020;23(2): E71‐E83.
- Sun X, Wang T, Cai D, et al. Cytokine storm intervention in the early stages of COVID-19 pneumonia. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020; S1359-6101(20):30048-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.04.002
- Diao Bo, Wang Chenhui, Tan Yingjun et al. Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Frontiers in Immunology. 2020; 11: 827. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00827
- Bari E, Ferrarotti I, Saracino L, Perteghella S, Torre ML, Corsico AG. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome for Severe COVID-19 Infections: Premises for the Therapeutic Use. Cells. 2020;9(4):E924. doi:10.3390/cells9040924
- Guidance document on appropriate management of suspect/confirmed cases of COVID-19. Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. (07.05.20). Retrieved from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/FinalGuidanceonMangaementofCovidcasesversion2.pdf
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Issues Emergency Use Authorization for Potential COVID-19 Treatment. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (07.05.20). Retrieved from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-issues-emergency-use-authorization-potential-covid-19-treatment
- Khoury M, Cuenca J, Cruz FF, Figueroa FE, Rocco PRM, Weiss DJ. Current Status of Cell-Based Therapies for Respiratory Virus Infections: Applicability to COVID-19 [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 7]. Eur Respir J. 2020;2000858. doi:10.1183/13993003.00858-2020
- Leng Z, Zhu R, Hou W, et al. Transplantation of ACE2- Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves the Outcome of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Aging Dis. 2020;11(2):216‐228. doi:10.14336/AD.2020.0228
- Golchin A, Seyedjafari E, Ardeshirylajimi A. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for COVID-19: Present or Future [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 13]. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;1‐7.
- Ji F, Li L, Li Z, Jin Y, Liu W. Mesenchymal stem cells as a potential treatment for critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 22]. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;10.1002/sctm.20-0083. doi:10.1002/sctm.20-0083
- Beasley MB. The pathologist’s approach to acute lung injury. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010; 134(5):719‐727. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-134.5.719
- Liang B, Chen J, Li T, et al. Clinical remission of a critically ill COVID-19 patient treated by human umbilical cord. ChinaXiv. (09.05.20) Retrieved from: http://www.chinaxiv.org/user/download.htm?id=30285







