It has been called the “sharing economy,” the “collaborative economy” and the “platform economy,” but whatever you call it, the gig economy has taken over the professional lives of many individuals. Millennials, who now make up the largest proportion of the labor force, according to Pew Research Center, have been spearheading the gig economy. While designers, developers, engineers and coders are starting to work as contractors, freelance scientists have also found a space in this economy.
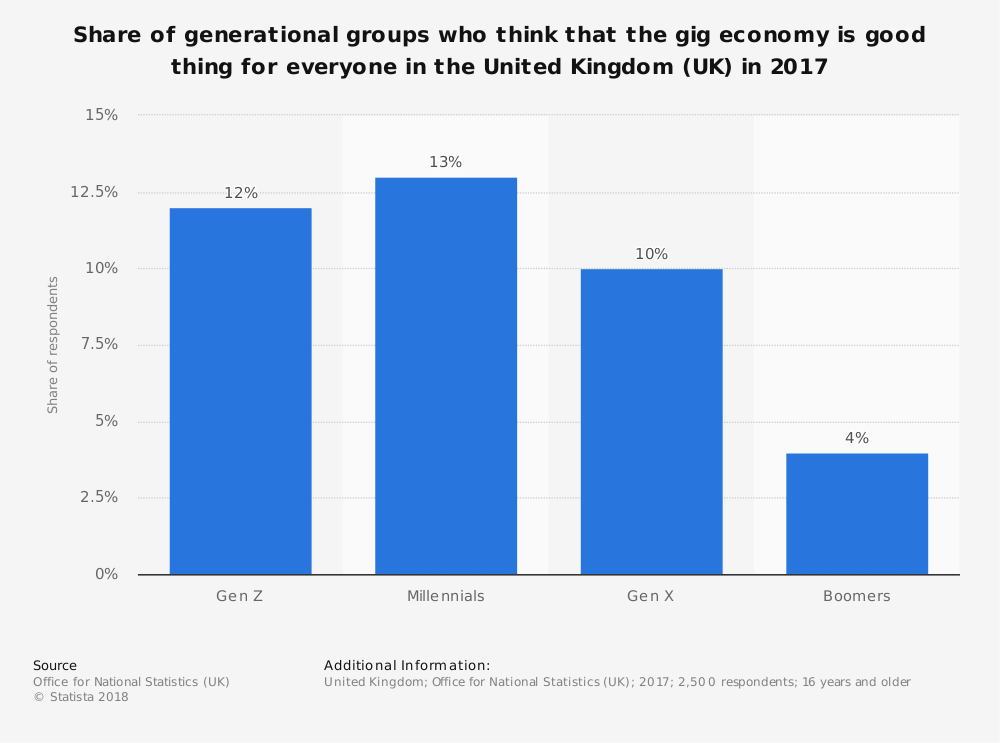
Share of generational groups who think that the gig economy is good thing for everyone in the United Kingdom (UK) in 2017
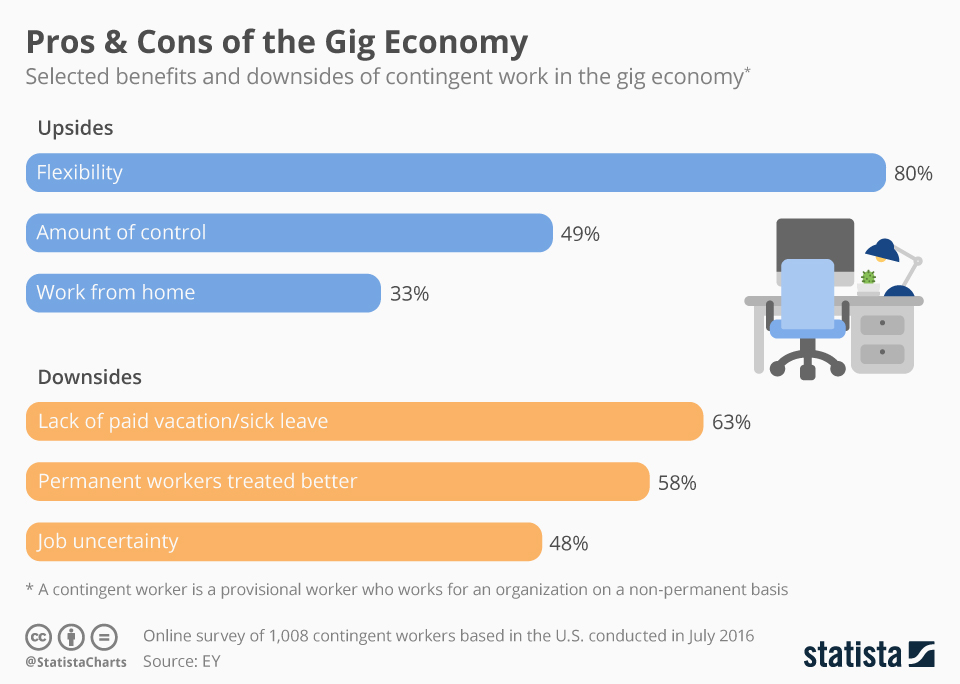
What Is the Gig Economy?
So, what is the gig economy? The gig economy is a type of on-demand, peer economy. Companies involved in the gig economy share specific characteristics. They often have a ratings-based marketplace as well as in-app systems of payment. They give workers the chance to earn money on a schedule they choose, and they do not have a full-time, specific position.
Some examples of these companies are Task Rabbit for service requests, Postmates for delivery of certain products, Airbnb for housing and hotel requests and Uber and Lyft for ride-hailing. Online marketplaces have a database of not just designers and developers, but also include highly skilled workers, with PhD-qualified experts offering freelance services on websites like Kolabtree.
It has been suggested that the gig economy could be the norm in the future and that having a “9 to 5” job Monday through Friday could be far less desirable than it is today. A study by the Freelancers Union and Upwork shows freelancers could make up a majority of the United States workforce within the next decade.
While tech has had a huge impact on the gig economy, another study by Harvard-Princeton from 2016 shows that less than one percent of the gig economy is based on technology platforms. The study presents that the gig economy is, in fact, based more on contractors, freelancers and part-time workers than just tech platforms.
Trends to Look for in the Gig Economy
While the gig economy is a recently evolved trend in the labor market itself, it has brought with it a number of other trends that will continue into the future. Here are some examples:
Artificial intelligence: The gig economy is huge on crowdsourcing platforms, which are expected to rely heavily on AI. Gig workers use crowdsourcing platforms to search for tasks and available jobs. AI can sort the applications and categorize the workers in order to find the best employee for that work.
Virtual Reality: Another trend is the use of virtual reality in the gig economy for communication. VR could change the way workers collaborate in this new workforce. Remote workers and in-office workers could use VR to collaborate and meet.
Other communication technologies: Technologies like Slack and JIRA can easily incorporate contractors into teams of workers and allow them to collaborate with the team and be in constant communication. Slack also allows the worker to leave the project or group at the end of the contract or work piece.
Mobile apps are helping both freelancers and companies taking advantage of the gig economy. There are a number of apps, like Shiftgig, which allow companies to find workers to fill empty positions on projects and jobs.
Advantages of the Gig Economy
Large talent pool: According to Accenture Technology Vision 2017, 85 percent of executives plan to increase their organization’s utilization of independent freelance workers over the upcoming year. They plan to do this because many workers are looking for the lifestyle that freelancing offers. Many tech projects these days are done by workers on a freelance basis. This way, businesses can source different work from large talent pools without having to stick to one individual or group.
Budget-friendly: The gig economy has another huge advantage for companies. Small businesses or startups can work with and hire experienced employees and developers for freelance work at a lower price and with a smaller commitment. This opportunity allows them to work with qualified people they originally would not have been able to hire full time.
Win-win situation: The gig economy allows workers to take on a flexible, work-whenever-you-like lifestyle that can work for both the employees and the company. Employees are given the chance to control their own professional careers while companies are able to take advantage of the blended workforce.
Disadvantages of the Gig Economy
While freelance work may sound like the dream, it does come with some downsides.
- Critics of the gig economy argue that workers in the freelance world lack protection and fair pay. For example, many freelance employees are not paid benefits like holidays or sick pay.
- Some reports even suggest that some freelance workers are not making minimum wage. It’s possible for freelance workers to be earning below minimum wage because companies are not obligated to pay their freelancers a specific salary since they are not full-time or even part-time employees.
Fixing the Disadvantages
While the disadvantages to working as a freelancer in the gig economy seem large, there are suggestions on how to address the issues. The Taylor Review, a review submitted to the UK government that addressed employee and worker rights in the UK’s labor law in 2017, made a series of suggestions and recommendations on how to reform workers’ rights and give them rights as freelance workers.
The Taylor Review suggested to the UK’s government that it create a new category of worker — the “dependent contractor.” The “dependent contractor” would have some benefits and wage protections.
The Trades Union Congress is a national trade union center in England and Wales that represents the majority of trade unions and has a total of around 5.6 million members. TUC has a mission to support trade unions and ensure they grow and thrive. They have a commitment to ensuring everyone earns a livable wage.
The TUC has taken a stand on the freelancer protection issue. They say that when employees are underpaid, including freelance employees, the government gets fewer dollars in taxes and insurance and ends up paying more in credits and benefits. The TUC calculated that the government could lose billions each year for underpaid workers.
Future of the Gig Economy
While there are some disadvantages to the gig economy, there are also attempts to fix them. It is obvious that many millennials who are entering the workforce do not want to be a part of the “old economy” and are taking the labor force by storm and changing it into what they want it to be.
Whatever happens to help combat the issues with the gig economy, we can expect more and more workers to join the freelance workforce, and change the way we get things done. It is up to businesses to utilize the opportunities this shift is presenting to them, and make full use of access to resources from the world over.







