Kolabtree freelance biostatistician consultant, Rudra Patel provides a comprehensive guide on how to develop a Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) for Clinical Trials.
1. Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) in a Clinical Trial (CT)
A well-written and complete Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) is important to increase the quality of clinical trials and make it more valid and generalized.
SAP is a defined outline of the planned statistical basic/advance methods for the analyses for a clinical trial and is written in study protocol as well as separately. SAP is crucial and is one of the key Regulatory confidential documents in the development of a clinical trial. An SAP is a more challenging task in a clinical trial protocol development that requires a strong command on statistical methodology, medical terminology and visualization power. It provides explicit guidance on statistical programming and the presentation of results for clinical trial. The following four important types of SAP are used in a clinical trial (Figure 1).
- Data monitoring
- Interim statistical analysis
- Integrated statistical analysis plan
- Statistical analysis plan for clinical study
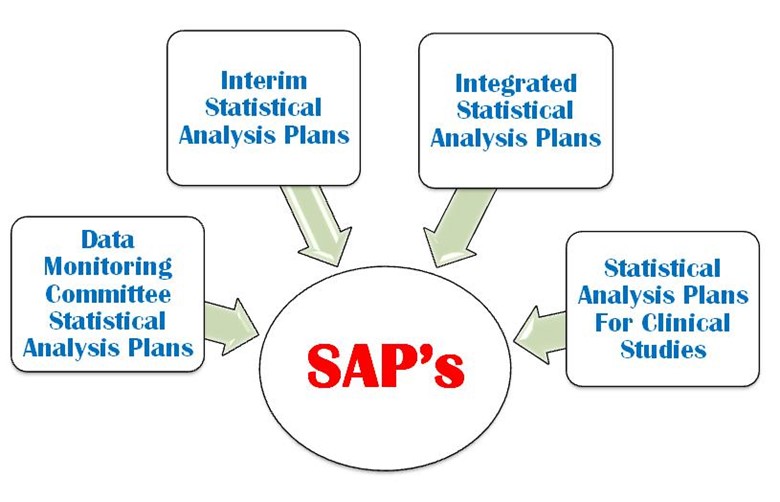
Figure 1: Four important types of SAP are used in a CT
The SAP is mostly written as a separate document or it is included in CT study protocol as a standard operating procedure for dealing with the statistical part of the clinical study. A team medical statistician/biostatistician is in-charge of developing the SAP in coordination with the principal investigator of the CT study. The document should be reviewed by Senior Biostatistician and finalized before to submission to the review board and regulatory authorities. If any protocol amendments are done, then the SAP is amended as well.
The SAP must properly explain following the aims and primary objectives, secondary objective, exploratory objectives, primary/secondary/exploratory endpoints, trial population, design of the trial, sample size calculations with justifications/assumptions, and the randomization methods. Additionally, an SAP must describe in detail the statistical methodology i.e. efficacy analysis, safety data analysis, reporting conventions, etc. Figure 2 shows the most important points that need to be considering when developing SAP in the clinical trial study protocol.
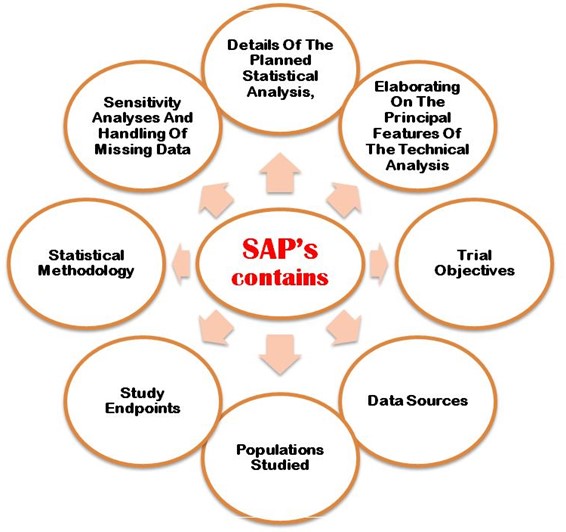
Figure 2: Detailed important points considering in when developing SAP in CT protocol.
The analysis plan developed should be reviewed special attention and approved by senior blinded biostatistician before database lock by authorities. Ahrweiler et al. 2011 conference paper published online explained the importance of review statistical analysis plan. The following detailed important points considering in when developing SAP in CT protocol,
- Detailed of the planned statistical analysis
- Elaborating on the principal features of the technical analysis.
- Trial objectives
- Data sources
- Population studied
- Study endpoints
- Statistical methodology
- Sensitivity analysis and missing data
The clinical trial SAP should be developing with an in-depth discussion between the study the principle investigators and statistician. Following are statistician role and responsibility,
- To write a research statement or hypothesis of the clinical trial study.
- Determine the primary endpoints and secondary endpoints.
- To find out and develop a strategy to reduce bias and sample size selection for clinical trial
- To define all appropriate statistical methods for clinical trial data analysis
In the development of SAP in the clinical trial need to explain in-depth key highlights points. Yuan et al.2019 published a special interest article on “Guide to the statistical analysis plan” [Figure 2]. The article provides in-depth the SAP of an actual clinical trial research study is to provide a practical detailed guide on writing an effective SAP. Additionally in the same paper discussed where what, why of an SAP, when and who, and highlight the key contents of the SAP. The need for clinical trial research study to well written and documented SAPs, particularly for regulatory studies.
2. Importance of the Statistical Analysis Plan in Clinical Trials
CT is conducted on all new drug/medicine development process and medical devices. Since last one decade, increasing the rate patients recruited into clinical trials for drug/medicine developments have been from Europe and the US as well as developing countries.
In clinical studies, SAP is one of the critically important documents. It ensures that the analyses to evaluate all pre-planned study hypotheses are conducted in a scientifically valid manner and that all decisions are documented. It also provides in-depth detail on how the results will be presented and reported in CT.
Clinical trials are used to assess the additional benefits and improve interventions in medical health care. The more important thing to consider while conducting a clinical trial is to execute the trial with minimum bias. Therefore, each clinical trial to have a clear and detailed SAP to its support to reproducibility. For the best practice of CT scientific research studies, reproducibility of research, and to avoid concerns of misuse of clinical research, a clear detailed and very transparent SAP much be needed, to improve trial conduct and reporting. Following are three essential roles of SAP needs to maintain in conducting CT.
- Transparency: Transparency concerning how the analysis will proceed by specifying in advances the methodology that will be applied
- Communication: Clear communication to everyone involved in the study on how to proceed
- Replication: Facilitates replication so that a future research team can follow the same steps to confirm the results on the same or a new sample.
As per standard guidelines with best practice, it’s important to the clinical trial project statistician/biostatistician prepares a study SAP before clinical trial start, detailing all the planned analyses, study parameters, including analysis set definitions and basic/ advance statistical methodology.
Additionally, some other important considerations relating to SAP in CT include:
- One way of minimizing bias is to blind the Biostatistician.
- The SAP should be documented in such a way that all the data manipulations and analyses performed can be replicated.
- A Trial Master File is required to be maintained with all the relevant documentation at trial completion by the Biostatistician.
The systematically arranged analysis plan helps the clinical trial team to be together on the same page and adds another layer of specificity to the CT. It describes the systematic planned statistical methodology of a clinical trial research study. As compare to the protocol of clinical trial the SAP is an in-depth technical document in which detailed statistical techniques for study designing and analyzing clinical trials data. While writing SAP we generally follow ICH E3 and E9 guidelines. This gives us an idea of the body content of individual sections of SAP. But E3 and E9 do not specify specific statistical techniques.
To improve reproducibility, transparency, and validity among clinical trials. National Institutes of Health (NIH) published “Rules for clinical trials studies registration and results information submission”, in that mandates trial registration, posting of clinical trial ongoing recruitment or results within ClinicalTrials.gov , and submission of the separate original document statistical analysis plan (SAP) along with the clinical trial research study protocol.
The big contribution of the medical statistician/biostatistician apart from developing a standard SAP is to the designing, monitoring and analyzing of clinical trial data.
3. Detailed checklist/guidelines for SAPs in clinical trials
In developing SAP of CT, we need to take into consideration all detailed checklist/standard guidelines. Important guidelines used in development in SAP are ICH E9 (International Conference for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use) and SPIRIT (Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials).
Transparency and reproducibility have been a fundamental term adding value in clinical trial data. However, the influence of statistical methodology directly affects on decisions making of clinical trial, well-documented, maintained confidentiality and transparent statistical conduct is essential. Expert medical statistician/biostatisticians can help develop SAPs in accordance with standard guidelines.
As per ICH E9 SAP usually known as reporting and analysis plans may also be known as Data Analysis Plans (DAP) or Statistical Analysis Plans (SAP) in other organizations. ICH E9 guidelines state that “the principal features of the eventual SAP of the data should be described in the statistical section of the protocol.” However, SPIRIT (Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials) guidelines refer to a separate SAP.
The SAP is a most essential document in CT which needs report to regulatory authorities (E.g. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA)). Standard guidelines suggest that SAP needs to stored in the confidentially clinical trial master file and it is used during regulatory authorizes audits to check if statistical documents followed exactly by standard guidelines.
The SAP is the most commonly used documents to guide statisticians. In general, the followings should be included in an SAP (Figure 3).
The statistician should be referred to The CONSORT Statement (and any extensions) and also ICH E9 Statistical Principles for Clinical Trials (PDF, 325 KB).
- Trial Planning & Design station
- The EQUATOR Network– A resource centre for good reporting of health research studies.
- The CONSORT website
- In 2017 the published guidelines by Gamble et al.2017, the guidelines of these articles recommend a minimum of 55 important items that should be considered when developing an SAP following.
- Title and registration
- Introduction
- Study methods
- Statistical principles
- Trial population
- Analysis
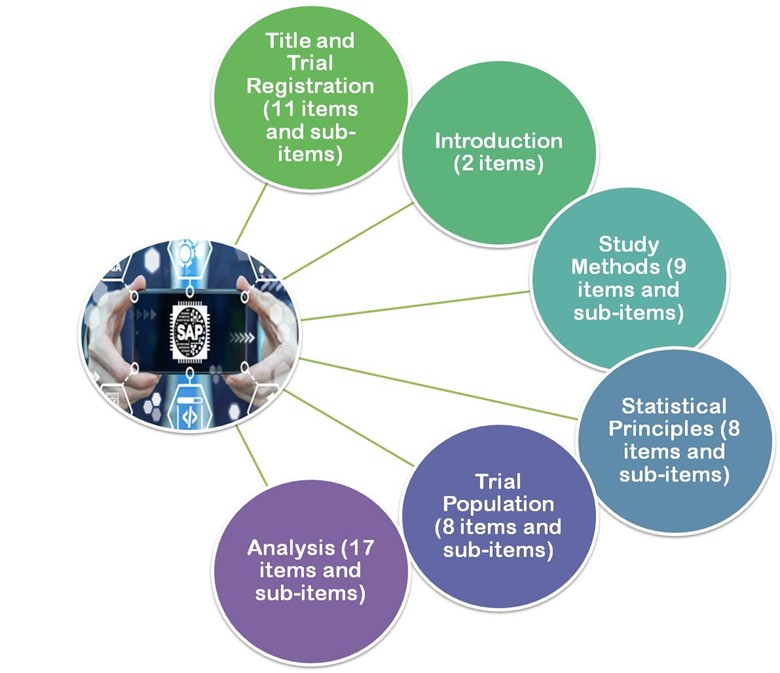
Figure 3: Gamble et al. 2017, the guidelines are divided into 6 major sections.
4. What does an SAP consist of?
A checklist of 32 detailed checklists for developing the Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) Checklist (Word). The primary intention of being more applicable to the final analyses of CTs as well as later-phase randomized CT. The most important guidelines developed by the FDA’s Guidance for Industry: Statistical Principles for Clinical Trials.
The following guidelines and recommendation for the content of an SAP:
- SAP is not a standalone document and should be read in conjunction with the clinical trial protocol.
- The clinical trial protocol should be consistent with the principles of the SPIRIT 2013 Statement.
- The SAP is to be applied to a clean or validated data set for analysis.
Detailed guidelines developed through funders, regulatory authorities, journals, industry representatives and UK Clinical Research Collaboration registered Clinical Trial Units (UKCRC CTUs). The Guidelines for the Content of Statistical Analysis Plans in Clinical Trials in-depth details describe in JAMA. However, a more in-depth detailed explanation of each checklist per item can be found in the elaboration document. The SAP statement also included is included in the Equator Network and MRC-NIHR Trials Methodology Research Partnership (TMRP). Following are key documents and key links used in developing SAP in clinical trial (Figure 4).
- Key document
- Checklist
- Elaboration
- JAMA paper
- Key links
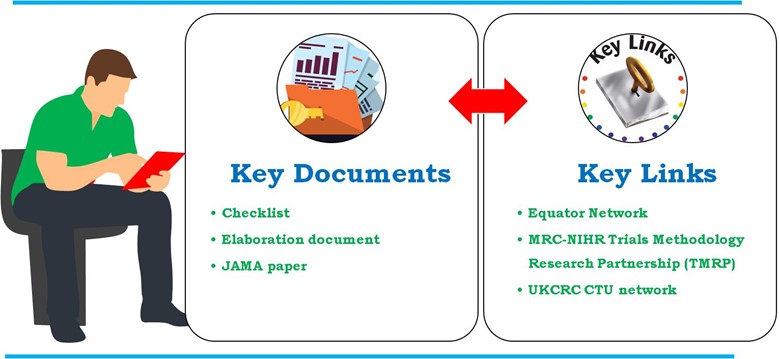
Figure 4: Key documents and key links used in developing SAP in clinical trial
5. Hiring a freelance clinical statistician for help with SAPs
Developing an SAP often requires the support of a freelance clinical statistician. With the help of an experienced biostatistician, you can develop a thorough and error-free SAP, that will improve the quality of your clinical trials.
Browse clinical trial consultants on Kolabtree now and get in touch with an expert directly.







